 基于Cola的初步实践
基于Cola的初步实践
这一节,主要是介绍CQRS、基于COLA的分包方式。
希望将领域模型的理论,应用到实战。
既然要应用到实战,这里不经要问一个问题: 距离实战,还有多少差距?
# 业务要求
1、活动策划可以查看所有用户信息,并可以通过,手机号码、姓名、销售信息 里的一个或多个来查找用户,显示姓名,号码。
2、活动策划可以查看用户的详细信息,显示:姓名,号码,新手福利信息;并修改用户的新手福利。
3、用户可以自行注销账号。
# 常见代码
应用服务:
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepo userRepo;
@Autowired
private CheckUserService checkUserService;
@Autowired
private RealnameService realnameService;
@Override
public UserDTO register(Name name, PhoneNumber phone) throws ValidationException {
// 查询实名信息(实名信息验证)
RealnameInfo realnameInfo = realnameService.get(name, phone);
// 构造对象
User user = new User(realnameInfo, phone);
// 检查User对象
checkUserService.check(user);
return new UserDTO(userRepo.save(user));
}
@Override
public List<UserDTO> findList(UserParamDTO userParamDTO) {
List<User> userList = userRepo.find(userParamDTO);
List<UserDTO> userDTOList = new ArrayList<>();
userList.forEach(user -> {
userDTOList.add(new UserDTO(user));
});
return userDTOList;
}
@Override
public UserDTO find(UserParamDTO userParamDTO) {
if (null == userParamDTO.getUserId() || userParamDTO.getUserId().length() == 0) {
return null;
}
User user = userRepo.findById(userParamDTO.getUserId());
if (null != user) {
return new UserDTO(user);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public UserDTO setFresh(UserParamDTO userParamDTO) {
if (null == userParamDTO.getUserId() || userParamDTO.getUserId().length() == 0) {
return null;
}
User user = userRepo.findById(userParamDTO.getUserId());
if (null != user) {
// 设置用户为新客身份,以便发送新手礼包
user.setFresh(true);
// 检查User对象
checkUserService.check(user);
return new UserDTO(user);
}
return null;
}
@Override
public Boolean deleteOne(UserParamDTO userParamDTO) {
if (null == userParamDTO.getUserId() || userParamDTO.getUserId().length() == 0) {
return false;
}
return userRepo.delete(userParamDTO.getUserId());
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
# 认识问题
1、前两章的问题,这里再次出现
解决办法,回顾前两篇内容。
2、随着不断的提取概念,经典的3层结构不能很好的容纳这些概念。
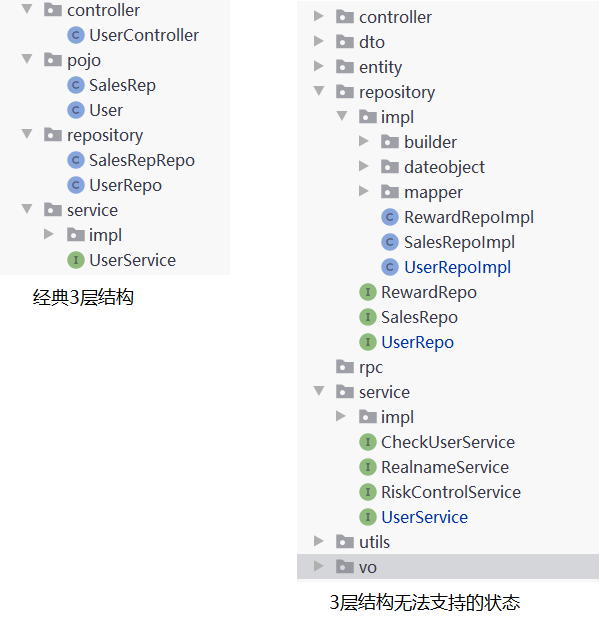
3、多个请求使用一个DTO,导致DTO臃肿
现在的UserParamDTO,被多个业务使用。导致DTO的臃肿,在传输中需要填充并不需要的字段。
后续维护者,不知道DTO的成员变量有几重业务意义;只能不断膨胀。
同时应用服务不断被修改,有业务外流的风险;也不符合开闭原则。
@Data
public class UserParamDTO implements Serializable {
// 用户id
private String userId;
// 用户名称
private String name;
// 用户手机
private String phone;
//绑定销售id
private String salesId;
// 标志是否为新用户,默认为false
private Boolean fresh;
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 1、解决分包不清晰
相对经典的3层架构而言,DDD也有自己的分层架构方式。
DDD的经典4层架构:用户接口层,应用层,领域层,基础设施层
与原3层架构,对照如下。
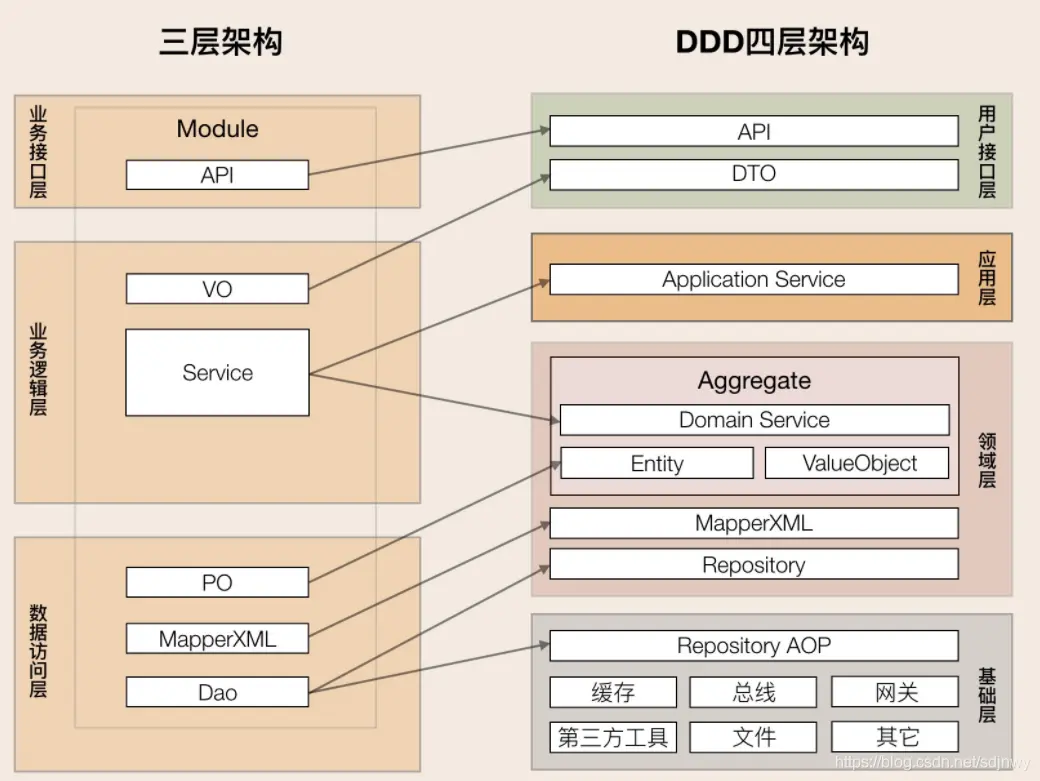
用于DDD分层的复杂性比较高,如: 具体代码如何划分,如何归属。
这里推荐使用Cola的分层方式。
目前Cola已经到4.0时代,经过4个版本的沉淀;笔者认为它已经是一个非常完善的架构方式。
# Cola 4.0 架构/框架
COLA 4.0 架构分成COLA架构和COLA组件两个部分:
COLA架构:关注应用架构的定义和构建,提升应用质量。
COLA组件:提供应用开发所需要的可复用组件,提升研发效率。
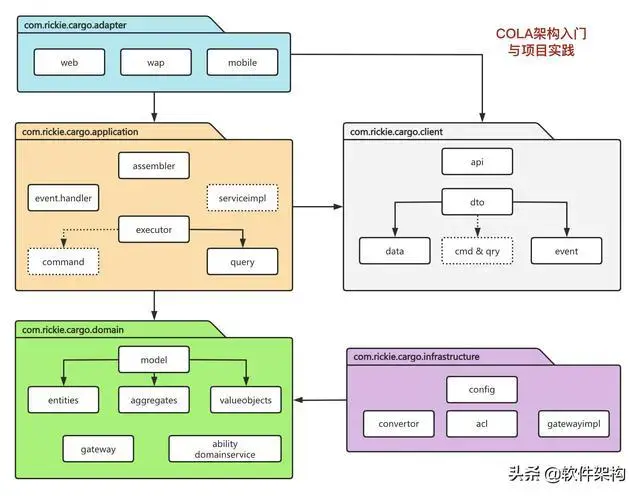
COLA架构各个包结构的简要功能描述,如下表所示:
| 层次 | 包名 | 功能 | 必选 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adapter层 | web | 处理页面请求的Controller | 否 |
| Adapter层 | wireless | 处理无线端的适配 | 否 |
| Adapter层 | wap | 处理wap端的适配 | 否 |
| App层 | executor | 处理request,包括command和query | 是 |
| App层 | consumer | 处理外部message | 否 |
| App层 | scheduler | 处理定时任务 | 否 |
| Domain层 | model | 领域模型 | 否 |
| Domain层 | ability | 领域能力,包括DomainService | 否 |
| Domain层 | gateway | 领域网关,解耦利器 | 是 |
| Infra层 | gatewayimpl | 网关实现 | 是 |
| Infra层 | mapper | ibatis数据库映射 | 否 |
| Infra层 | config | 配置信息 | 否 |
| Client SDK | api | 服务对外透出的API | 是 |
| Client SDK | dto | 服务对外的DTO | 是 |
# 分包后工程结构
1、首先是用户接口层和应用层的填充。
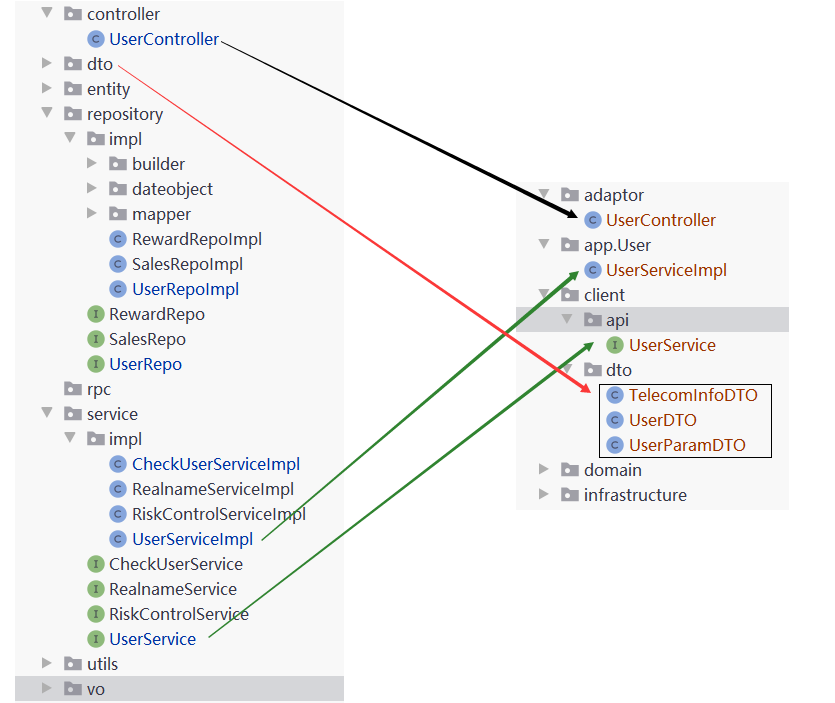
2、领域层的填充
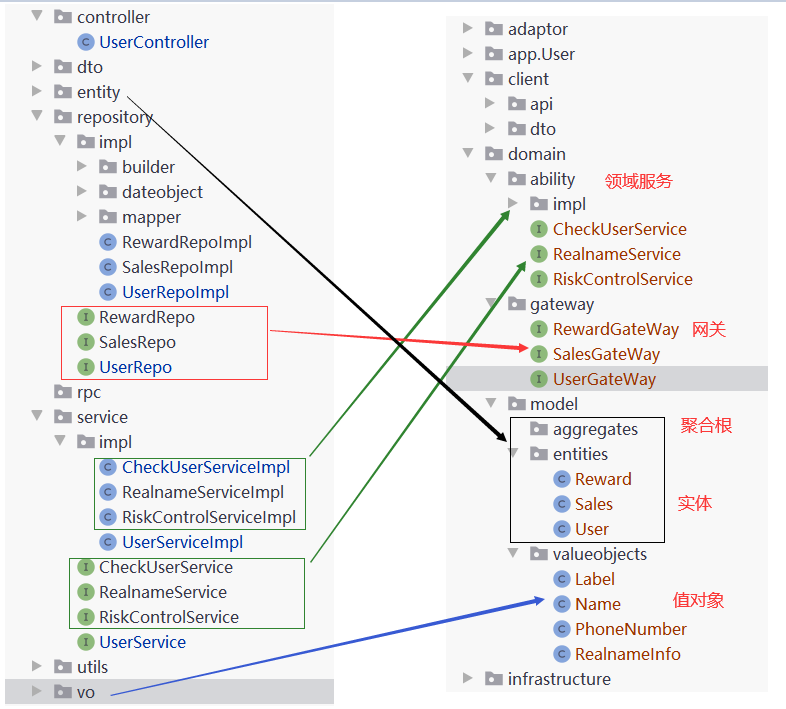
3、基础设施层 的填充
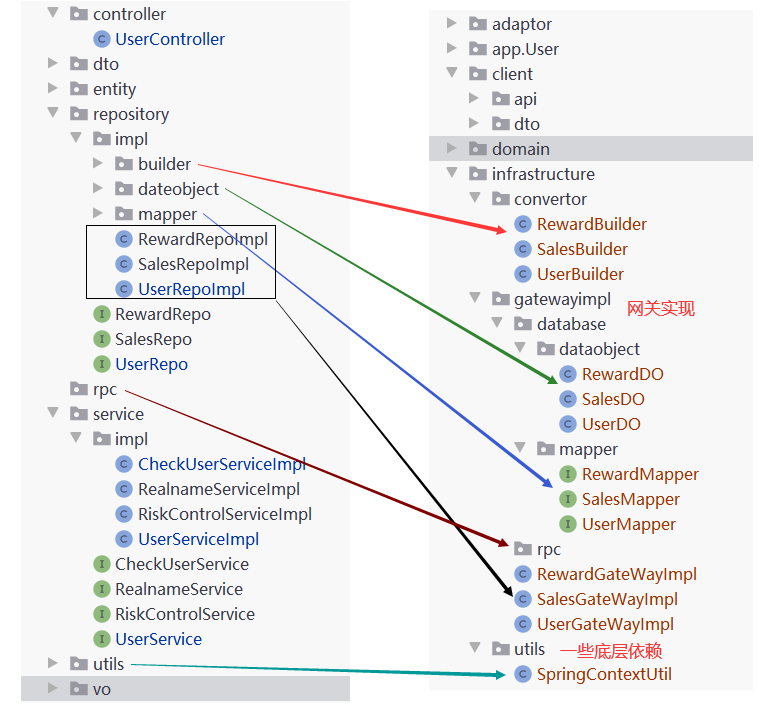
# 2、解决DTO臃肿问题
当前的DTO运行方式为:
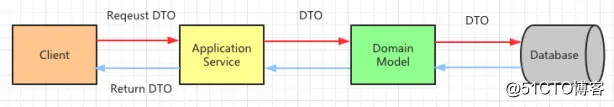
单一的DTO,在DDD中适配多个业务。DTO不断的被复杂化。
为了解决这个问题,这里引入一个概念:
CQRS(Command and Query Responsibility Segregation)命令和查询责任隔离
为了解决传统DTO在DDD中的问题,提出了根据读写职责不同,把领域模型切分为command和query两个部分:
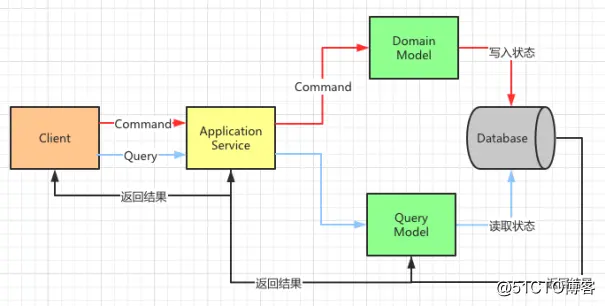
Command端与Query端都通过Application Service 进入系统,共享同一个数据库,但Command端只写入状态,Query端只读取状态。
代码分包方式:
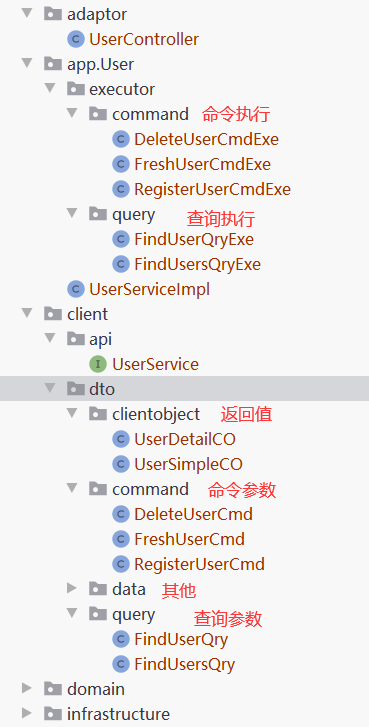
定义和执行体:
// 参数
@Data
public class RegisterUserCmd extends Command {
// 用户名称
private String name;
// 用户手机
private String phone;
}
// 执行
@Component
public class RegisterUserCmdExe {
@Autowired
private UserGateWay userGateWay;
@Autowired
private CheckUserService checkUserService;
@Autowired
private RealnameService realnameService;
public SingleResponse<UserDetailCO> execute(RegisterUserCmd registerUserCmd) {
try {
// 查询实名信息(实名信息验证)
RealnameInfo realnameInfo = realnameService.get(new Name(registerUserCmd.getName()), new PhoneNumber(registerUserCmd.getPhone()));
// 构造对象
User user = new User(realnameInfo, new PhoneNumber(registerUserCmd.getPhone()));
// 检查User对象
checkUserService.check(user);
return SingleResponse.of(new UserDetailCO(userGateWay.save(user)));
} catch (ValidationException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return SingleResponse.buildFailure("401", e.getMessage());
}
}
}
// 返回值
@Data
public class UserDetailCO implements Serializable {
// 用户id
private String userId;
// 用户名称
private String name;
// 用户手机
private String phone;
//用户标签
private String label;
//绑定销售id
private String salesId;
// 标志是否为新用户,默认为false
private Boolean fresh;
public UserDetailCO(User user) {
this.userId = user.getUserId();
this.name = user.getName().getName();
this.phone = user.getPhone().getPhone();
this.label = user.getLabel().toString();
this.salesId = user.getSales().getSalesId();
this.fresh = user.getFresh();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
调用代码:
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
RegisterUserCmdExe registerUserCmdExe;
@Autowired
FindUsersQryExe findUsersQryExe;
@Autowired
FindUserQryExe findUserQryExe;
@Autowired
FreshUserCmdExe freshUserCmdExe;
@Autowired
DeleteUserCmdExe deleteUserCmdExe;
@Override
public SingleResponse<UserDetailCO> register(RegisterUserCmd registerUserCmd) {
return registerUserCmdExe.execute(registerUserCmd);
}
@Override
public MultiResponse<UserSimpleCO> findList(FindUsersQry findUsersQry) {
return findUsersQryExe.execute(findUsersQry);
}
@Override
public SingleResponse<UserDetailCO> find(FindUserQry findUserQry) {
return findUserQryExe.execute(findUserQry);
}
@Override
public SingleResponse<UserDetailCO> setFresh(FreshUserCmd freshUserCmd) {
return freshUserCmdExe.execute(freshUserCmd);
}
@Override
public Response deleteOne(DeleteUserCmd deleteUserCmd) {
return deleteUserCmdExe.execute(deleteUserCmd);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
封装完成后,任何一个业务的参数变化,只会影响自己的业务情况。
应用服务不会因为业务的变化而变化,具体的业务组织交个每个业务执行体做; 更符合单一职责。
# Git代码
仓库位置:https://github.com/su-dd/demo.git (opens new window)
代码位置:领域模型/30Demo (opens new window)
# Cola组件介绍
COLA 组件:提供了一些框架级别的功能,提供应用开发所需要的可复用组件,提升研发效率。
| 组件名称 | 功能 | 版本 | 依赖 |
|---|---|---|---|
| cola-component-dto | 定义了DTO格式,包括分页 | 1.0.0 | 无 |
| cola-component-exception | 定义了异常格式,主要有BizException和SysException | 1.0.0 | 无 |
| cola-component-statemachine | 状态机组件 | 1.0.0 | 无 |
| cola-component-domain-starter | Spring托管的领域实体组件 | 1.0.0 | 无 |
| cola-component-catchlog-starter | 异常处理和日志组件 | 1.0.0 | exception,dto组件 |
| cola-component-extension-starter | 扩展点组件 | 1.0.0 | 无 |
| cola-component-test-container | 测试容器组件 | 1.0.0 | 无 |
参考:《 COLA 4.0:应用架构的最佳实践 (opens new window)》
梳理文档时,借用了多篇文档的内容,目前以记不清晰;未能详细标记,望海涵。
